
CS160: Foundations in Programming: Summer 2016
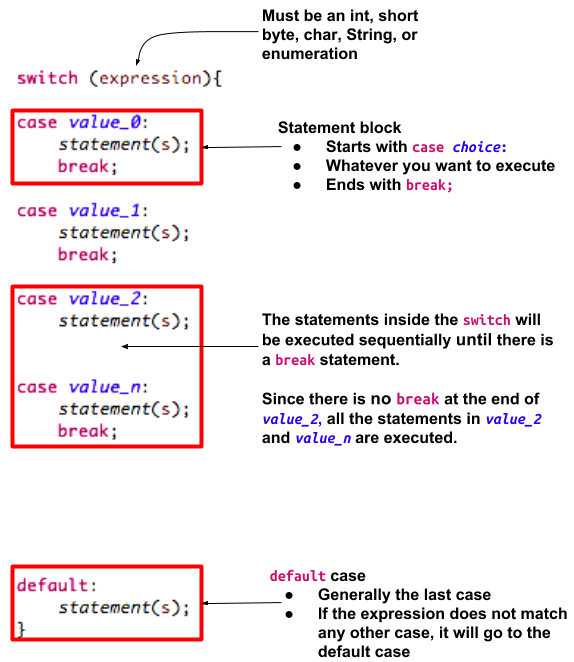
int day = 5;
String tomorrow = "";
switch(day){
case 0:
System.out.println("It's not the weekend! Let's work!");
tomorrow = "Tuesday";
break;
case 1:
System.out.println("It's not the weekend! Let's work!");
tomorrow = "Wednesday";
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("It's not the weekend! Let's work!");
tomorrow = "Thursday";
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("It's not the weekend! Let's work!");
tomorrow = "Friday";
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("It's not the weekend! Let's work!");
tomorrow = "Saturday";
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("It's the weekend! Let's go outside!");
tomorrow = "Sunday";
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("It's the weekend! Let's go outside!");
tomorrow = "Monday";
break;
default:
System.out.println("Not a valid day of the week!");
tomorrow = "?";
}
System.out.println("Tomorrow is: " + tomorrow);
String firstName = "kamaji";
switch (firstName) {
case "chihiro":
System.out.println("You must help your parents!");
break;
case "haku":
System.out.println("You are the river spirit!");
break;
case "zeniba":
System.out.println("You are a powerful witch!");
break;
case "kamaji":
System.out.println("You toil in the boiler room!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Are you a character in Spirited away?.");
break;
}
Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Please enter a letter: ");
char myChar = keyboard.next().charAt(0); // what's going on here?
switch (myChar) {
case 'L': case 'l':
System.out.println("L is for the way you look at me,");
break;
case 'O': case 'o':
System.out.println("O is for the only one I see,");
break;
case 'V': case 'v':
System.out.println("V is very, very extraordinary,");
break;
case 'E': case 'e':
System.out.println("E is even more than anyone that you adore can.");
}
In this example, what happens when the user types "Elephant"? How about "W"?