See this page as a slide show
CT320 Security
Thanks to:
- Dr. Indrajit Ray, CSU,
- Dr. James Walden, NKU,
- and Russ Wakefield, CSU
for the contents of these slides.
Topics
- Introduction
- Vulnerabilities, threats and attacks
- Risk Management
- OS Hardening
- PAM
- Passwords
- Firewalls & Intrusion Prevention Systems
Overview
- Computer Security
-
protection afforded to an automated information system in order to
attain the applicable objectives of preserving the integrity,
availability and confidentiality of information system resources
(includes hardware, software, firmware, information/data, and
telecommunications).
Security Objectives
- Confidentiality
-
Prevent / detect / deter improper disclosure of information
- Integrity
-
Prevent / detect / deter improper modification of information
- Availability
-
Prevent / detect / deter improper denial of access
to services provided by a system
Some Examples
- An employee should not know the salary of the manager (confidentiality)
- An employee should not be able to update own salary record (integrity)
- Salary slips should be printed on the last day of the month (availability)
Security Goals
- Data confidentiality
- Customer account data (credit cards, identity)
- Trade secrets
- Administrative data (passwords, configuration)
- Data integrity
- Administrative data
- Software downloads (patches, free tools)
- Web pages
Security Goals
- System integrity
- System/network availability
- Network bandwidth
- Network services (auth, file, mail, print)
- Disk space
Interesting Situation
You are the security admin of a company. One
day you notice that an employee is
downloading a very big file. You notice that
downloading a file is not exactly against
company policy. Should you flag this as a
security issue?
An Even More Interesting Situation
User uploads some financial documents on Microsoft
Cloud. You (Microsoft) analyze these documents and
determine that user owes back taxes to the IRS …
Security Objectives (continued)
- Prevention is more fundamental
- Detection seeks to prevent by threat of punitive action
- Detection often requires systems that must be prevented from alteration
- Sometimes detection is the only option
- Modification of messages on a network
More Security Objectives
- Authenticity — The property of being genuine and being able to be
verified and trusted
- Note similarity with integrity
- Accountability — Requirement that actions of an entity should be
traceable to that entity
- Non-repudiation — Requirement that an entity is not able to deny or
reject the validity of its past action
- Needed for proper accountability
Computer Security Challenges
- Not simple
- Must consider potential attacks
- Procedures used may be counter-intuitive
- Involve algorithms and secret info
- Must decide where to deploy mechanisms
Computer Security Challenges
- Battle of wits between attacker / admin
- Not perceived on benefit until fails
- Requires regular monitoring
- Too often an after-thought
- Regarded as impediment to using system
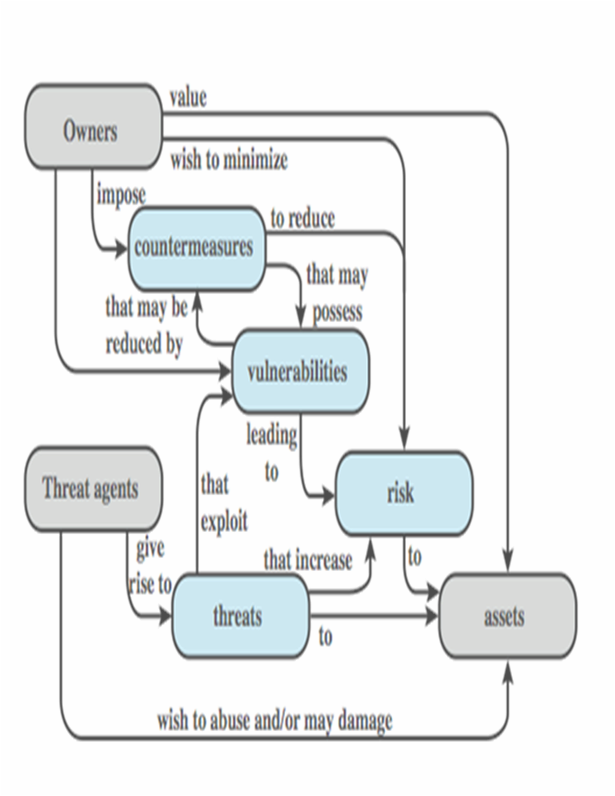
Systems Security Components / Terminology
- Owners
- Threat agents
- Assets
- Vulnerabilities
- Threats
- Countermeasures
- Risk
History
- WarGames
- 1983 movie that brought security to light
- Young man finds a back door into a military super
computer to run a nuclear war simulation, believing
it to be a computer game. Causes a national nuclear
missile scare and nearly starts WW III
- 1988 — Morris worm
- Millions of dollars and thousands of hours wasted
- First real global attack
- Still a wide open issue
Security by Obscurity
- If we hide the inner workings of a system, it will be secure?
- ¡Bad idea!
- Less and less applicable in the emerging world of
vendor independent open standards
- Less and less applicable in a world of widespread
computer knowledge and expertise
Security by Legislation
⚢ ⚤ ⚣
- If we instruct our users on how to behave, we can secure a system?
- ¡Bad idea!
- User awareness and cooperation is important but
cannot be the principal focus for achieving security
- Human beings tend to defy authority
Weakest Link In Computer Security
- Human beings are often considered the weakest link
- 95% of all attacks were directed against the home computer user in 2007
- Go ahead—just try to prevent your relatives from installing malware!
- End-users are frequently exposed to security risks
through routine on-line activities such as checking
email or web browsing
- Many recent attacks indicate that end-users are
increasingly becoming a new form of threat in
cyber-space, the so-called unwitting accomplice
Vulnerabilities, Threats and Attacks
- System resource vulnerabilities
- Be corrupted (loss of integrity)
- Become leaky (loss of confidentiality)
- Become unavailable (loss of availability)
- Attacks are threats carried out and may be
- Passive
- Active
- Insider
- Outsider
Vulnerabilities
- Bad/default passwords.
- Unused services with open ports.
- Unpatched software vulnerabilities.
- Transmitting confidential data in cleartext.
- Open modems or wireless networks.
- Physical access to critical systems.
- Uneducated users.
Vulnerability Databases
- Repository for vulnerability data
- Security checklists
- Security related software flaws
- Misconfigurations
- Impact metrics
- National Vulnerability Database (NVD)
Some Common Security Threats
Threat Motives
- Financial motives
- Identity theft
- Phishing
- Spam
- Extortion
- Botnets
- Political motives
- Danish sites hacked after Mohammed cartoons.
- Personal motives
- Just for fun.
- Insider revenge.
Threat Consequences
- Unauthorized disclosure
- Exposure, interception, inference, intrusion
- Deception
- Masquerade, falsification, repudiation
- Disruption
- Incapacitation, corruption, obstruction
- Usurpation
Attacks
- Classified as passive or active
- Passive attacks are eavesdropping
- Release of message contents
- Traffic analysis
- Are hard to detect so aim to prevent
- Active attacks modify/fake data
- Masquerade
- Replay
- Modification
- Denial of service
- Hard to prevent so aim to detect
How Systems Are Attacked
- Burglarize office ⇒ Obtain backup media ⇒ Steal customer data
- Bribe admin at ISP ⇒ Intercept email ⇒ Steal customer data
- Hack remote user’s home system ⇒ Intercept email ⇒ Steal customer data
- Hack SMTP gateway ⇒ Intercept email ⇒ Steal customer data
- Hack SMTP gateway ⇒ Hack thru firewall into internal network ⇒
Hack into fileserver ⇒ Steal customer data
Types of attacks
- Social engineering
- Cold calls, shoulder surfing, phishing,
- Alleviated by training, communication, etc.
- Software vulnerabilities
- Buffer overflows, known bugs
- Patching
- Configuration errors
- Complex — takes time and knowledge to do it right
- Easy to bypass
Risk Management
Risk is the relationship between your assets,
the vulnerabilities characteristic to those
assets, and attackers who wish to access or
modify those assets.
Security Tips
- Packet filtering
- Unnecessary services
- Software patches
- Backups
- Passwords
- Vigilance
Rules of Thumb
- Don’t put files of interest on your system (good luck with that)
- Security policy should specify how info is handled
- Don’t provide homes for hackers
- Set traps to detect intrusions
- Monitor reports from your security tools
- Teach yourself about security
- Be nosy—prowl around looking for unusual activity
Password management
- Poor password management is common weakness
- Indirect information
- Passwords easily hacked
- Steps
- Run the common password checker often
- Check for null passwords
- Or just don’t permit them in the first place
- Password maintenance
- Password aging
- No group logins
sudo
SetUID programs
- Prone to security holes
- Minimize the number of them
- Use pseudo-users with just the required privilege, rather than using root
- Disable on public filesystems, e.g., USB auto-mounter
Security issues
- Remote event logging
- Secure terminals
- Configure to disable root logins from SSH, VPNs, etc
- Best to just disable root logins from anywhere, except perhaps the
system console.
- NIS — known to have security issues
- NFS4 — security enhancements
- Sendmail — runs as root
Security issues — continued
- Viruses and worms
- Not widely prevalent on Linux
- Less market share than Windows
- Access controlled environment
- Trojan horses
- Programs get Trojan horses embedded in them
- Keep software up to date
- Rootkits
- Hiding system information
Assets
- Login account
- Network bandwidth
- Disk space
- Data
- Reputation
Defenses
- Vulnerability mitigation
- Use secure authentication systems.
- Deploy software in secure configuration.
- Patch security flaws quickly.
- Attack mitigation
- Firewalls to prevent network attacks.
- IDS to detect attacks.
- Virus/spyware scanners.
OS Hardening
- Make it difficult:
- Secure the physical system.
- Install only necessary software.
- Keep security patches up to date.
- Delete or disable unnecessary user accounts.
- Use secure passwords.
- Disable remote access except where necessary.
- Use
sudo instead of su.
- Run publicly accessible services in a jail.
- Check logs regularly.
- Configure firewall on each host.
- Run security scanner to check security.
- Document security configuration.
Secure the physical system
- Place servers in a physically secure location.
- Physically secure the case.
- Place ID tags on all hardware.
- Password protect the BIOS.
- Disable booting from removable media.
- Security cameras (detection, not prevention)
Install only Necessary Software
- Put different services on different hosts.
- A compromise in the web server shouldn’t compromise mail.
- Improves reliability and maintainability, too.
- Common unnecessary packages
- X-Windows
- Software development (gcc, gdb, etc.)
Security Patches
- Subscribe to vendor security patch list.
- Or know vendor’s update schedule.
- Patch Tuesday: MS Windows updates on second Tuesday of the month
- Update test host first.
sudo apt update; sudo apt dist-upgrade
- Patches can sometimes break services.
- Update other hosts after that.
- May need to schedule downtime if reboot required.
Use Secure Passwords
- Attacks against Passwords
- Password sniffing
- Password guessing via login
- Password cracking
- Defenses
- Do not transfer passwords over the network.
- Secure
/etc/{passwd,shadow}
- Configure password quality/aging rules.
- Test your passwords by cracking them.
- Use the most up-to-date password encryption!
PAM
Problem:
- Many programs require authentication.
- New authorization schemes require rewrites.
- longer passwords, keys, one-time passwords
Solution:
- Separate authentication from programs.
- Store authorization in Pluggable Authentication Modules.
- Programs choose PAMs to use at runtime by reading config files.
PAM Configuration
- Configured under
/etc/pam.d
- Each PAM-aware service has a file there.
Format: module-interface control-flag
module-name module-arguments
- Module-interface: one of 4 module types.
- Control-flag: how module will react to failure or
success (multiple successes may be required.)
- Module-name: PAM shared library.
- Module-args: Files to use, other options.
Module Interfaces
- auth — Authenticates use of service. For
example, it may request and verify a password.
- account — Verifies that access is permitted, e.g.
check for expired accounts or location/time.
- password — Sets and verifies passwords.
- session — Configures and manages user sessions,
e.g. mounting user home directories or mailboxes.
Module Stacking Example
rlogin PAM requirements
- The file
/etc/nologin must not be present.
- Root may not login over network.
- Environment variables may be loaded.
~/.rhosts entry allows login without password.
- Otherwise perform standard password login.
PAM config file:
auth required pam_nologin.so
auth required pam_securetty.so
auth required pam_env.so
auth sufficient pam_rhosts_auth.so
auth required pam_stack.so service=system-auth
Control Flags
required — Module result must be successful for
authentication to continue. User is not notified on
failure until results on all modules referencing that
interface are available.
requisite — Module result must be successful for
authentication to continue. User is notified
immediately with a message reflecting the first failed
required or requisite module.
sufficient — Module result ignored if it fails. If a sufficient
flagged module result is successful and no required
flagged modules above it have failed, then no other
results are required and the user is authenticated to
the service.
optional — Module result is ignored. Only necessary for
successful authentication when no other modules
reference the interface.
Password Quality
- Use
pam_cracklib.so in system-auth
- Options:
retry=#: Maximum # of retries.
minlen=#: Minimum password length.
lcredit=#: Min # of lower case letters.
ucredit=#: Min # of upper case letters.
dcredit=#: Min # of digits.
ocredit=#: Min # of other chars.
Password Aging
- Configure
/etc/login.defs before creating accounts:
- PASS_MAX_DAYS: Max # of days before password expires.
- PASS_MIN_DAYS: Min # of days before user can change pw.
- PASS_WARN_AGE: # of days for pw change notice given.
- Also configure
/etc/default/useradd:
- INACTIVE: # of days after pw expiration that account is disabled.
- EXPIRE: Account expiration date in format YYYY-MM-DD.
- Remember old passwords with
pam_unix.so:
- Prevents users from changing password back to old value.
- Modify
/etc/pam.d/system-auth
- Set pam_unix.so option remember=26
- Create
/etc/security/opasswd to store old passwords.
Disable Unnecessary Accounts
/etc/passwd contains application accounts.
- Delete unnecessary application accounts.
- uucp, games, gdm, xfs, rpcuser, rpc
- All should have locked passwords.
- Set shell to
/bin/noshell or /bin/false.
- Disable user accounts immediately on termination of employment.
- “immediately” doesn’t mean “soon”. It means “before”.
- Sure, keep the data around, but lock the account.
Disabling Remote Access
- Disable cleartext protocols
- telnet, ftp, rsh, rlogin
- Remove the packages, or
chmod -x the executables.
- Of course, a future update may “fix” the file permissions.
- Disable root access via ssh.
- Set
PermitRootLogin to “no” in sshd_config
- Remove root non-terminal consoles
- Disable password access via ssh
sudo
- Login as root only for single-user mode.
- Use
sudo instead of su.
- On my system,
root has no password.
One simply cannot log in as root; su always fails.
- Advantages:
- Uses user password instead of root’s password.
- Logs who executed what commands as root.
- Can delegate limited powers to some users.
Jails
- Complete isolation: virtual machines.
- Partial isolation: chroot
chroot /var/httpd httpd
- chroot filesystem needs:
/var/httpd/etc: limited /etc/{passwd,shadow,group}
/var/httpd/usr/lib shared libraries
/var/httpd/bin: extra binaries
/var/httpd/var/log: log space
/var/httpd/tmp: temporary space
Check Logs
- Review logs every morning.
- Better yet, have a program scan them.
- Send logs to a central server for
- security: attacker can’t hide tracks by deleting
- ease of use: you can read all logs in one place
Firewalls and Intrusion Prevention Systems
- effective means of protecting LANs
- internet connectivity essential
- for organization and individuals
- but creates a threat
- could secure workstations and servers
- also use firewall as perimeter defense
- single choke point to impose security
Firewall Capabilities & Limits
- capabilities:
- defines a single choke point
- provides a location for monitoring security events
- convenient platform for some Internet functions
such as NAT, usage monitoring, IPSEC VPNs
- limitations:
- cannot protect against attacks bypassing firewall
- may not protect fully against internal threats
- improperly secure wireless LAN
- laptop, PDA, portable storage device infected outside then used inside