Foundations and Interpretability in Machine Learning
Description:
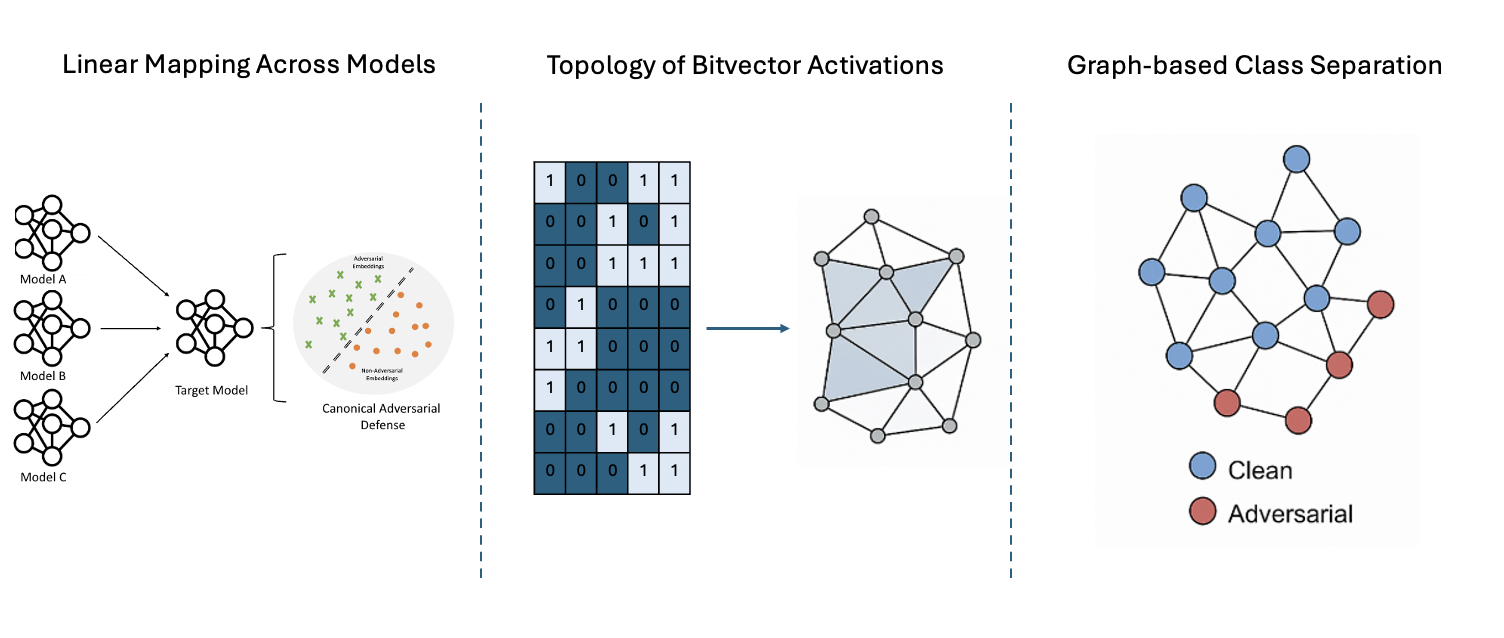
This project explores the internal representations of deep neural networks to understand model behavior, interpretability, and robustness. Starting with the insight that embeddings from different architectures can be linearly mapped to one another—even in the adversarial setting—we demonstrate that adversarial representations exhibit a shared geometric structure across models. This motivates a model-agnostic approach to adversarial defense using simple linear mappings, validated through cross-model generalization and classification.
Building on this foundation, we investigate the internal activations of networks at the bit level by encoding ReLU outputs into binary activation patterns (bitvectors). These discrete patterns enable efficient representation and open up new analysis tools grounded in topology and graph theory. Specifically, we model ReLU activations as convex polyhedral decompositions and construct dual graphs to trace how adversarial signals traverse a network. This approach identifies discriminative neurons critical for adversarial detection.
Finally, we quantify similarity across image representations by computing Hamming distances between bitvectors and constructing similarity graphs. Applying spectral techniques such as Laplacian eigenmaps and Fiedler partitioning, we show that deep networks gradually enhance class separability and encode adversarial distinctions in a structured way. Our results consistently show that bitvectors retain meaningful information with reduced dimensionality and achieve high accuracy in adversarial image detection using simple classifiers.
Together, these studies present a unified framework for understanding and utilizing internal representations—both continuous and binary—across models and training paradigms, contributing to the broader goals of explainability and trustworthy AI.
Publications:
Jamil, Huma, et al. "Hamming similarity and graph Laplacians for class partitioning and adversarial image detection." Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2023.
Jamil, Huma, et al. "Dual graphs of polyhedral decompositions for the detection of adversarial attacks." 2022 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data). IEEE, 2022
Jamil, Huma, et al. "Leveraging linear mapping for model-agnostic adversarial defense." Frontiers in Computer Science 5 (2023): 1274832.